
Parasitic Zoonoses
When a parasite that usually resides inside or on an animal’s body causes a disease in human beings, the disease caused by it is known as parasitic zoonosis. There are many types of parasites that reside in and on animals’ bodies. Pet animals like dogs and cats also have them and can become an important source of transmission of these parasites to humans if not taken good care of.
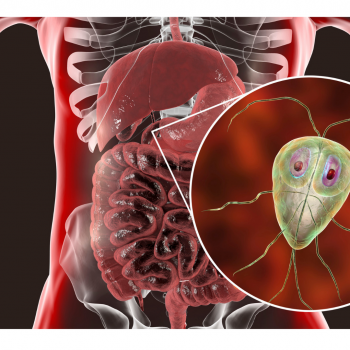
Giardiasis
It is a diarrhoeal disease transmitted by a parasite called Giardia duodenalis. This parasite resides in the intestine and also passes through feces. It can survive from a week to few months in the environment. Human infection is rare. Giardia spp. are very common enteric parasites of domestic animals, including livestock, dogs, and cats and wildlife. Giardia duodenalis causes giardiasis in humans and most mammals and therefore giardiasis is considered as a zoonotic disease.
This parasite lives on the mucosal surface of the small intestine. Here, it attaches and multiples. After multiplication, cysts form and travel into the large intestine and then to feces. These cysts can survive for several months however the adult forms cannot. Transmission occurs via fecal-oral route, or direct contact with an infected host or environment.
In humans-
- Gas
- Diarrhoea
- Greasy stools
- Cramps
- Dehydration.
- These symptoms usually begin with diarrhoea on the first day and slowly progress. Some rare symptoms include fever, itchy skin, swelling of joints and hives.
In animals-
- Weight-loss
- Diarrhoea can be observed which may be intermittent or continuous.
- Soft, pale, mucous stools
- Giardiasis in animals is often asymptomatic
Microscopic examination of the stools is done to identify Giardia cysts. Staining of the saline stool samples with iodine helps in the identification of Giardia. To detect the parasite, IFA and ELISA are commercially available. Examination of the stools with floatation technique and ELISA can give an accurate confirmation of the infection.
Good hand hygiene should be practiced for the prevention and control of Giardiosis. Toys should be cleaned, sanitised and disinfected. Children or animals with diarrhoea should be isolated. Good diaper practices should be adopted for very young children. Avoid swelling water in public swimming pools and try to reduce contact with animal feces.
Always wash your fruits and vegetables thoroughly. Cleaning and disinfection of the furniture in your house routinely will also help in keeping this infection at a distance.
